Many eco-friendly building materials have surfaced to diminish the environmental impact of building construction and operations. The materials include:
Reclaimed Steel – Reclaiming steel drastically reduces the amount of newly manufactured steel and thus greatly reduces the carbon footprint. Steel is more enduring than timber and strengthens structures against climatic concerns such as winds or earthquakes, as well as being repellent to pests/water/fire. Steel is well suited for roofing and structural support as there is no danger of warping. Steel has been used to create multiple carbon-neutral buildings and is 100% recyclable.
Reclaimed Wood – Reclaimed Wood can be harvested from abandoned structures including retired barns, ships, decommissioned buildings, salvage yards, railroads, and pallets. It can be employed as structural framing, flooring, external enhancement, and cabinetry.
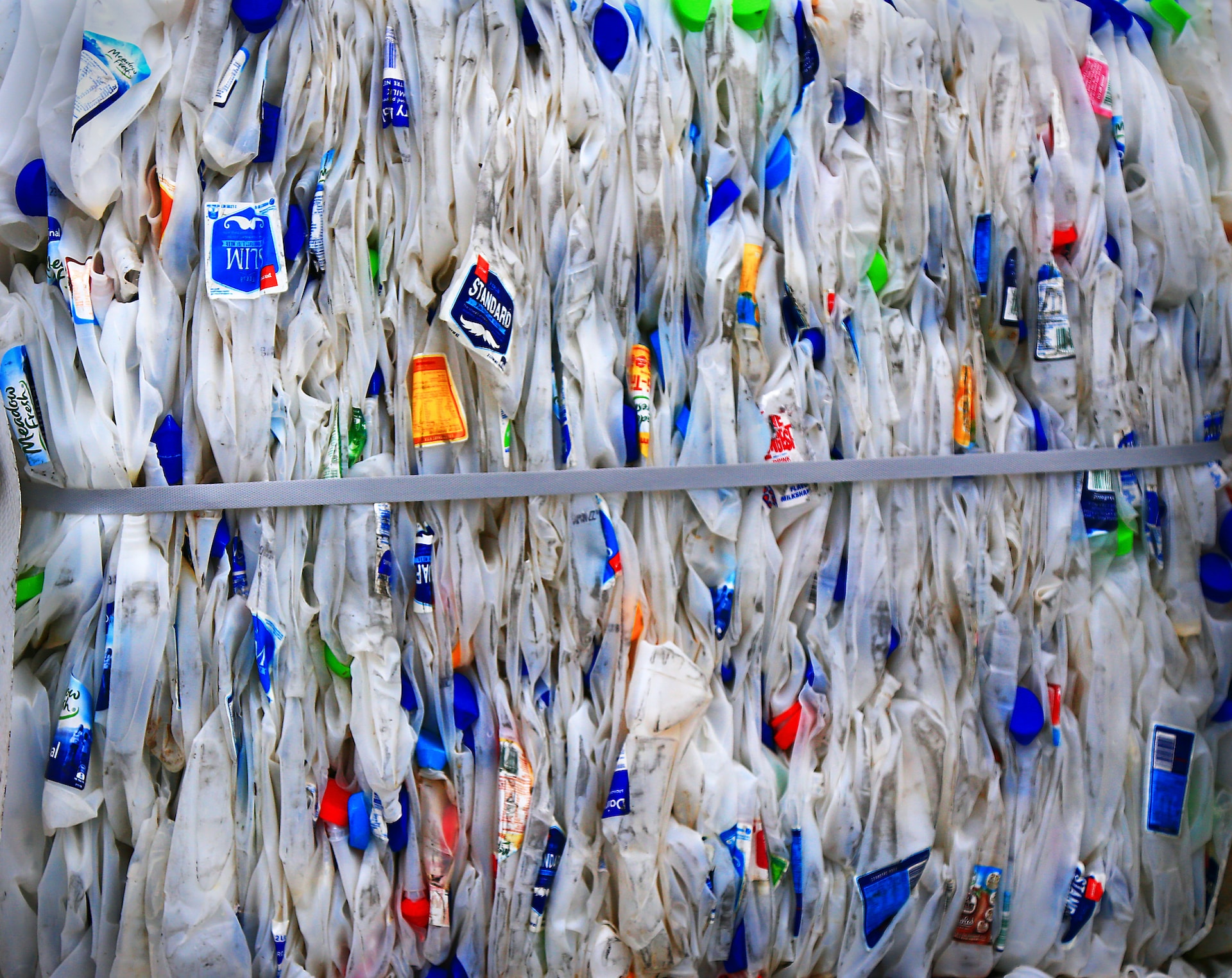
Recycled Plastic – The practice of grinding up recycled plastic is beginning to replace the expensive and pollution-heavy process of mining materials to manufacture concrete. It not only significantly reduces the carbon footprint of concrete production, but it also makes the entire process more affordable. The potential future of recycled plastic construction includes recycled plastic roads, bricks, concrete, pipes, roofs, and floors.
Rammed Earth – Made from compacted natural materials such as earth, gravel, and lime. rammed earth can be an affordable route for creating a durable structure with strong foundations. Rammed earth also delivers protection against pests, is completely non-toxic, and is highly resistant to fire.
Precast Concrete Slabs – Precast concrete slabs require less energy in the manufacturing stage and are more sustainable than conventional concrete. They can be utilized for walls, exteriors, roofing, and floors since they remain durable throughout all weather conditions. A structure built from precast concrete slabs can be easily deconstructed for further reuse.
Ferrock – Ferrock is a new material created primarily from iron-rich ferrous rock mixed with recycled materials such as waste steel dust or components of ground-up glass. Ferrock is up to five times stronger than conventional concrete and is even more flexible, making it more likely to resist earthquake damage. The manufacturing process of Ferrock is also carbon negative, as the material absorbs and binds carbon dioxide.
Straw Bales – Straw is a waste product and is frequently burned at the end of a farming season as it does not provide enough nutrients to become animal feed. Straw can be used in load-bearing walls, door and window frames, and doors, as well as finishes with a mix of lime, cement, and/or sand. It is one of the most cost-effective thermal insulation materials available and is very resistant to fire because when compacted, straw bales become almost airtight.
Sheep Wool – Sheep wool insulation performs as well as fiberglass but with many added benefits. Amino acids in wool bond with the molecules of harmful chemicals and can effectively filter the indoor air. In addition, wool absorbs moisture, suppresses mold, resists fire, and has excellent thermal qualities.
Bamboo – Technically a grass, Bamboo can be harvested at a much faster rate than trees (just 1-5 years) and does not need to be replanted as regrowth is regenerated by its root system, making it one of the cheapest and fastest recyclable building materials. It is the superior option for flooring and cabinetry as it toughens over time and has even greater strength than concrete or brick.
Cork – Cork can be harvested from a living tree, rendering it to be one of the most eco-friendly reclaimed building materials on the planet. It is flexible, lightweight, and almost completely impervious to moisture. It has various applications in flooring, countertops, acoustic wall coverings, roofs, and rigid insulation.
For more information on how LA Creed is having a sustainable, environmentally friendly impact on your community visit https://creedla.com.