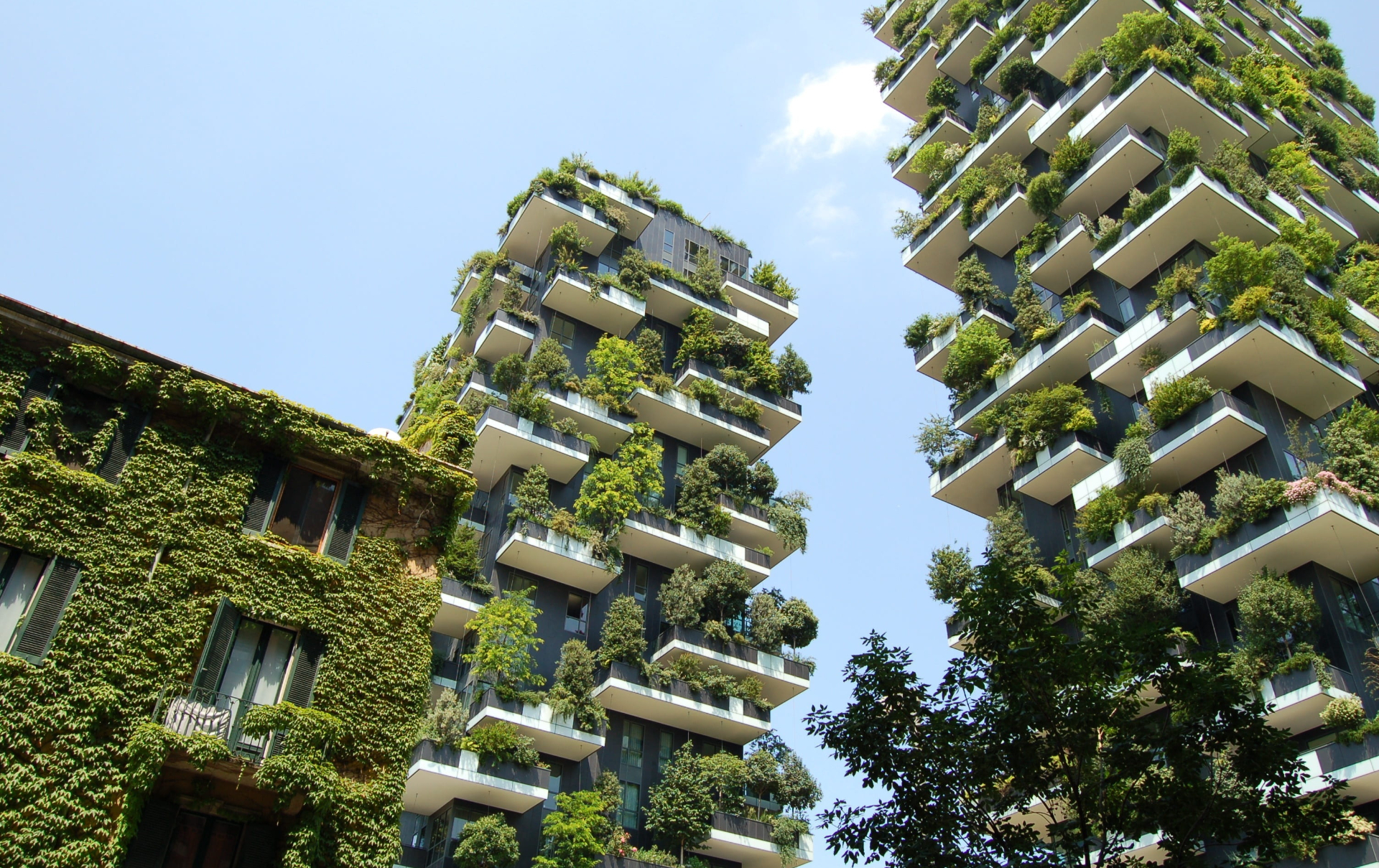
For April, CREED LA is highlighting and addressing Sustainable/Environmentally Friendly
Buildings.
Definition
An environmentally friendly building is one that:
- Utilizes building materials that are non-toxic, ethical, and sustainable. Sustainable building materials include items such as wood, bamboo, adobe, coconut, bioplastics, stainless steel, and straw.
- Employs renewable energy, such as solar energy. A zero net energy building (ZNEB) is optimally efficient, and over a year, generates energy onsite, using clean renewable resources, in an amount equal to or greater than the total energy consumed onsite.
- Chooses windows that are energy efficient and keep the heat inside. An energy-efficient window has argon, krypton, or other gasses between the panes. These odorless and colorless non-toxic gasses insulate better than regular air.
- Operates with efficient use of water– such as harvesting rainwater for irrigation. Water efficiency is the use of a minimum amount of water to accomplish more functions. It relies on water-saving technologies to use water in a smarter way (i.e., water-efficient products, fixtures, and appliances).
- Deploys pollution and waste reduction measures that enable reuse and recycling. Construction projects often use more materials than are needed due to design choices and over-specification. For example, it is possible to attain the same structural strength of a building using only 50 to 60 percent of the specified cement. New technologies, such as 3D printing for foundations and supporting structures, can reduce the number of materials needed through innovation in structural forms. Another example is that today only 20 to 30 percent of construction and demolition waste is reused or recycled. A more deliberate disassembly effort could facilitate more material reuse and recycling, which together could prevent 0.6 billion metric tons of CO2 emissions every year.
California Examples
A few models to mimic include:
- Paradise High School – In 2018 The worst wildfire in California’s history, burned down 19,000 structures ruining 50% of the district’s schools, and killed 85 people. The population of Paradise plunged from 26,800 to 2,034. The design for the new high school will feature fire-resistant construction, CMU (concrete masonry unit) construction, metal framing, exposed metal versus exposed wood, cementitious siding instead of true wood siding, metal roofing, and fire sprinklers.
- Fairview Heights in Inglewood – Features 150,000 square feet of affordable housing. The
final design has more than 100 units including ground floor retail space, a community
police center, youth and adult educational space. One of the most impressive features is the extensive solar panel array on its roof. In addition, the architects of KFA have opted for wall-mounted heat pumps instead of standard mechanical condensers that could be installed on the parapet walls around the perimeter of the roof. The PV system was designed to produce enough onsite electricity to support the nearly 14,000 square feet of common space, which contains a large community room with a teaching kitchen, a computer lab, case management and resident service offices, and conference rooms.
- Parkside North in Long Beach – The dormitory at California State University, Long Beach (CSULB) is a four-story, 127,000-square-foot complex that includes 474 beds in various configurations, kitchen and dining areas, study pods, and outdoor gathering spaces. The building will feature net-positive energy, and net-zero water, 90% of student rooms will face north-south, have operable windows, a high-performance rainscreen, and 235 solar panels.
For more information on how Creed LA is having a sustainable, environmentally friendly impact on your community visit https://creedla.com.